RREES: SEADS Vault
Alexa Modular Adapter
Alexa Enabled Universal Remote
ARbot
AutoIrrigation
Automated Hydroponics
Autonomous UV-C Sanitation Bot
Bus Tracker Project
Bus Tracking System
Bus Usage Monitor
Classmates Search
Cloud Native Wireguard
CO2 Monitoring System
Diabetics Companion
Edu Plastic Pollution
EDU (CPU)
Googun
H2Eyes
IMDB on FPGA
Indoor Robot
Induction Motor
Land Trust Management
Learning Storage Networks
Low Latency Gaming
Marine Plastics Monitor
ODS Web App Performance Tuning
Offroad Spotting Drone
ONI Code Visualization
Painless Healthcare Management
Parquet+OCI project
Preventing Vehicular Heatstroke
Remote Nuclear Monitoring
Rent-a-Driveway 2020
ResearchConnect
RREESS Microgrid Management
Save our Species 2020
SAWbots - Miniature Medical Robots
Self Stabilizing Personal Assistance Robot
Slug Charge
Slug Sat
Smart Cane
Smart Magazine Floorplate
Smart Park
Smart Seat Cover for Posture Detection
Smart Slug Bin
Soaring Slugs
Team Litter Buster
Understanding Healthcare Data
Vibrace
VoIP Management Assistant
Wildfire Detection Drone
Abstract
When the power grid fails, the failure can be life threatening. The Resilient Reliable Efficient Energy Systems (RREES) Lab aims to deliver power quality data fast enough to keep the failure from becoming an emergency, detailed enough to identify the failure, and comprehensive enough to locate the failure. While the Smart Energy Analytic Disaggregation System (SEADS) handles the collection of an overwhelming quantity of data ( ~5.5GB per day per device uncompressed), our team built the SEADS Vault to:
- identify important events in the SEADS data,
- notify homeowners of events,
- inform grid managers of event locations
Overview
How Outages are traditionally handled:
- A User calls their provider to manually report.
- Perform a scheduled/monthly maintenance.
- Voltage is measured at the substation
How we want to change it:
- Automated Event Detection and notification
- Isolate problem areas and fix faulty equipment
- Voltage is monitored at the consumer’s house
All these factors provide better system health:
- Monitors on the Consumer level leads to higher accuracy and can be used to link common events to or faulty equipment.
Approach
Architecture Diagram
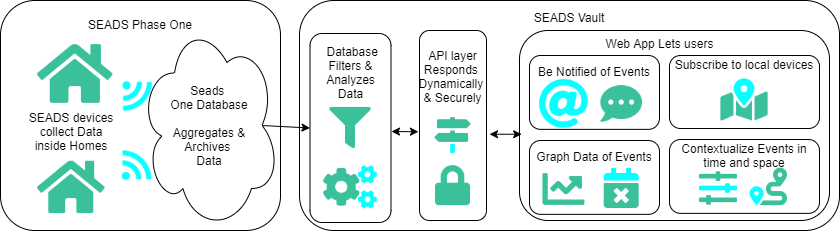
Technology used includes React, Flask, and PostgresQL for development. We incorporated as third party services, such as Auth0, Mapbox, and Twilio; in order to handle account management, geolocation, and notifications. Finally, we used Skyhook for partitioning on each SEADS Device.
Issues

Downed power lines can cause safety issues like wildfires.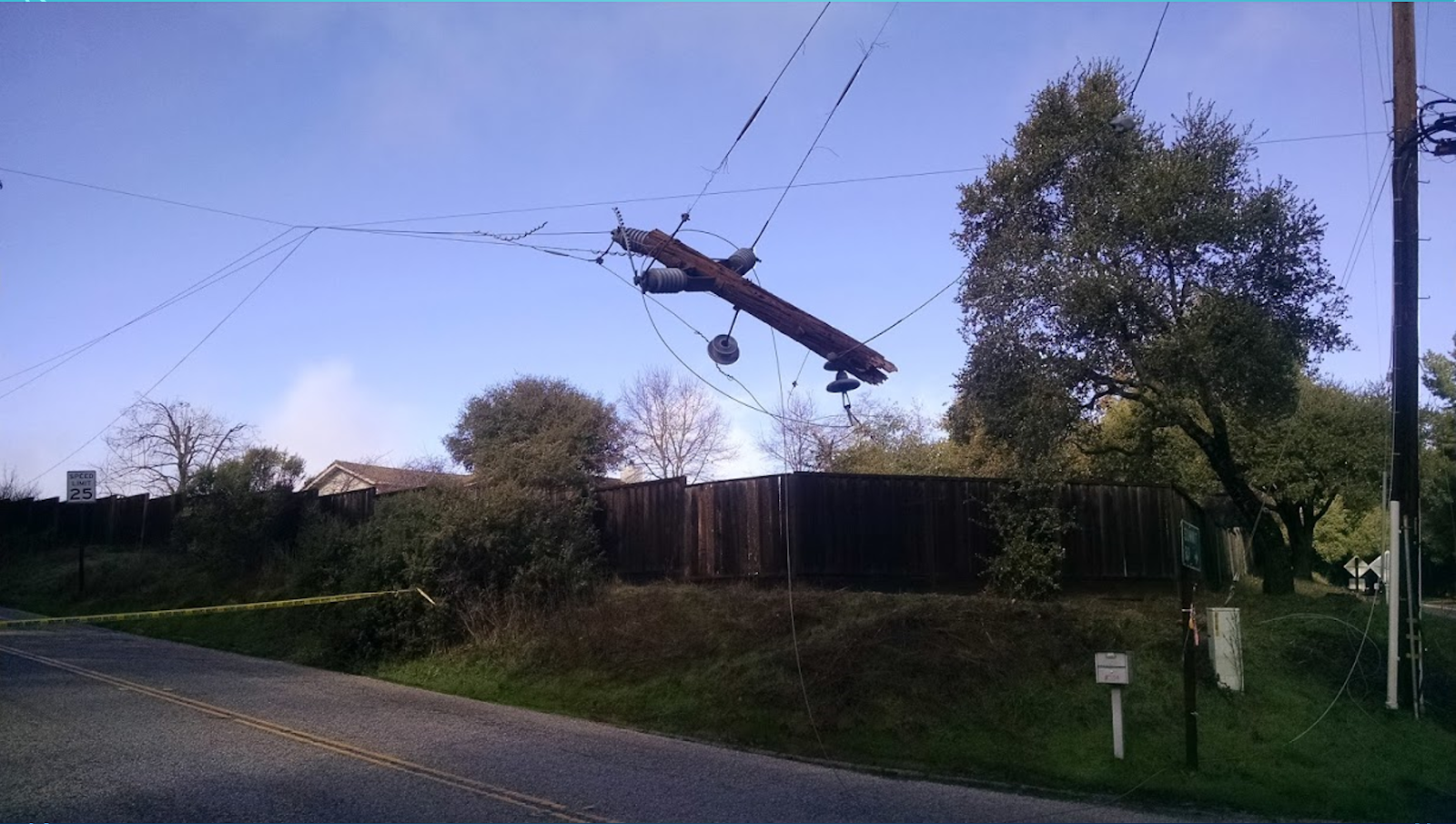
Here, a tree falls down in an urban area and is not detected for a long time. This causes a power outage and a road obstruction.
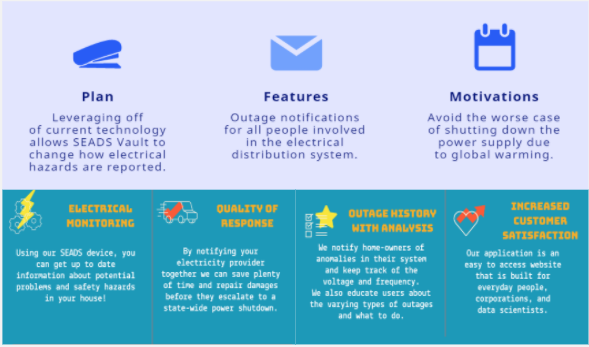
SEADS Vault Features
1. Have an application deployed to the web.
2. Display real time live voltage to end user.
3. Notify consumers of potential outages in interested areas via email and text.
4. Flag defective equipment for repairs ASAP to improve safety and improve reporting.
Conclusion
We hope to establish a strong foundation for future innovators to build new features using SEADS and extend the user base outside of Santa Cruz. For instance, researchers and scientists could use the data to develop machine learning models.
Acknowledgements
Brian Zhao: Phase 1 Design
Patrick Mantey: Mentor and Sponsor
Jeff LeFevre: Creator of Skyhook and Design
Michael Choi: Building the SEADS Hardware
Faeze Brahman: Managing Weekly Scrum
Akila De Silva: Managing Weekly Scrum
Richard Jullig: Bi-Weekly Check instructor